Aluminum anodizing is the process of creating a protective oxide layer on the surface of aluminum, which improves its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appearance. Initially, Aluminum anodizing was primarily used to improve the appearance of aluminum products. However, over time, it became apparent that anodizing also improved the durability and corrosion resistance of aluminum, leading to its widespread adoption in many industries. Advancements in anodizing technology have led to the development of new anodizing methods, making it a critical part of modern manufacturing. Read More…
At Tompkins Metal Finishing, we offer mid to high volume aluminum anodizing. We do pre-cleaning, etching, deoxidizng, dyeing and sealing. We can achieve a wide range of surface finishes from bright to dull matte in clear, black, gold, blue and red. Other methods are also available with consideration of alloy, coating thickness, masking requirements and racking instructions.
Pioneer offers many custom finishing solutions to make your products perform at the highest levels. We are experts in providing specialized finishes to improve the performance for your specific component parts. Whether your product design requirements include finishes to make your product resist corrosion, last longer, look better, slide more freely, bond securely to another material, or many...

At All Metals Processing of Orange County, we specialize in providing high-quality aluminum anodizing services that enhance both the performance and appearance of metal components. We take pride in our ability to deliver precise, consistent finishes that improve corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal across a wide range of applications.

At Automatic Anodizing, we specialize in providing high-quality aluminum anodizing services designed to enhance both the appearance and performance of aluminum parts. With decades of experience, we have built a reputation for precision, consistency, and reliability in every project we handle. Our advanced anodizing processes improve corrosion resistance, wear protection, and surface hardness...

Dajcor Aluminum is the leading Canadian supplier of extruded, fabricated/machined and anodized components and assemblies to the automotive, renewable energy, transportation, building trades, military, recreation, and consumer-product industries.
More Aluminum Anodizing Companies
Aluminum Anodizing Process Explained: Methods and Benefits
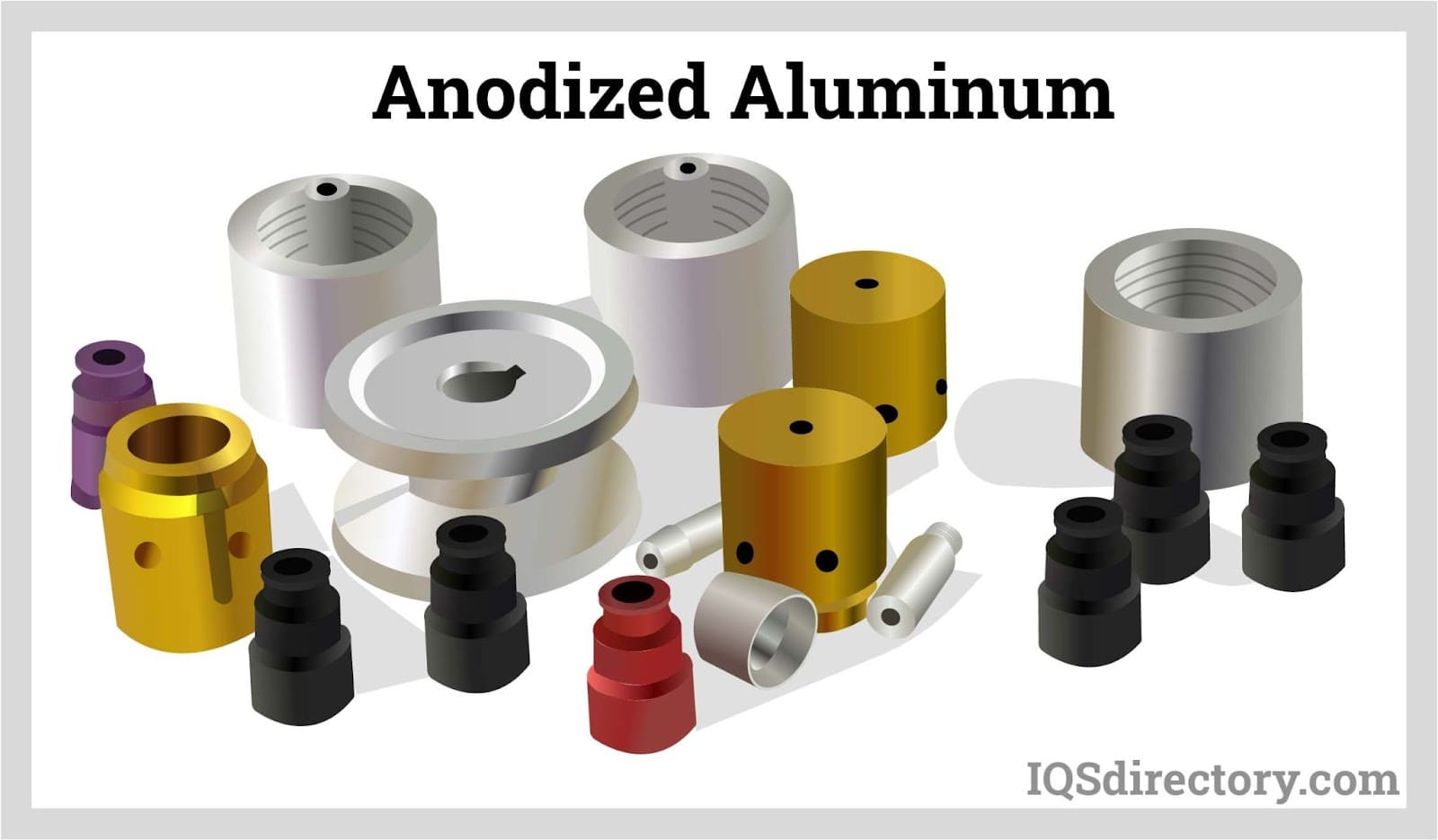
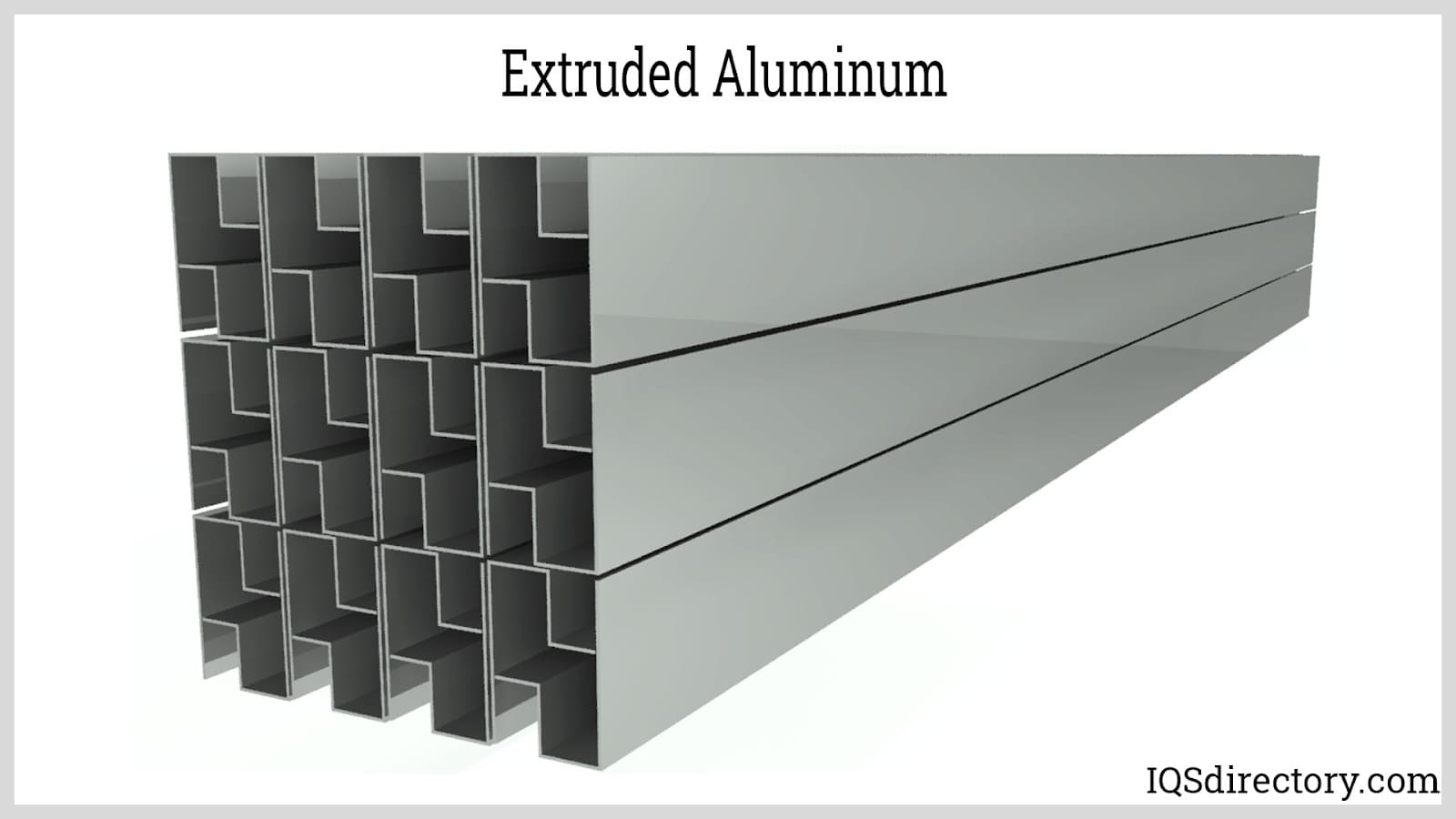
The aluminum anodizing process is a highly specialized surface treatment that enhances the durability, performance, and aesthetics of aluminum products. In this process, an aluminum part is submerged in an electrolyte solution and an electric current is passed through it. This controlled electrochemical reaction causes the surface of the aluminum to oxidize, forming a robust layer of aluminum oxide that is integral to the metal itself, rather than a coating applied on top. This durable, corrosion-resistant layer can be engineered for a variety of industrial, architectural, and commercial uses.
There are several types of anodizing processes tailored to specific performance requirements, each with unique characteristics and advantages:
- Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II): The most common and versatile method, widely used across industries. Aluminum parts are submerged in a sulfuric acid electrolyte and subjected to a direct current. This process creates a moderately thick (typically 0.0005″–0.001″ thick) anodic coating, renowned for superior corrosion resistance, increased hardness, and the ability to be dyed in a vast array of colors. Typical use cases include architectural panels, automotive trim, and consumer electronics. However, the sulfuric acid anodized layer is not highly electrically insulating, which is a consideration in electrical applications.
- Chromic Acid Anodizing (Type I): Used primarily for specialized applications that demand a thin, highly conductive anodic layer. Aluminum parts are immersed in a chromic acid bath, resulting in a thinner and softer coating than Type II. Key benefits include outstanding electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making this process ideal for the electronics and aerospace industries. However, due to the toxicity and hazardous nature of chromic acid, strict environmental and workplace safety regulations apply, and its use is increasingly limited in favor of greener alternatives.
- Hard Anodizing (Type III): This advanced technique produces an extra-thick and extremely durable anodic layer by employing higher voltages and lower temperatures. Hard anodized coatings (up to 0.002″) offer exceptional wear resistance, superior hardness, and the best corrosion protection among anodizing methods. Hard anodizing is favored for aerospace, defense, and precision engineering applications where surface durability is paramount. While hard anodizing provides fewer color options and usually results in a darker, more utilitarian finish, its mechanical properties are unmatched.
Choosing the Right Process of Aluminum Anodizing
Selecting the optimal aluminum anodizing process for your application can significantly impact product performance, appearance, and lifecycle cost. The right choice depends on several critical factors:
- Desired Properties: Identify if the final product needs maximum corrosion resistance, increased hardness, electrical insulation, or decorative appeal.
- Intended Use & Industry Standards: Consider the application’s environment (indoor, outdoor, marine, medical, etc.) and any industry-specific requirements such as those found in aerospace (AMS 2471/2472) or architecture (AAMA 611).
- Design & Geometry: Evaluate the size, shape, and complexity of the part. Anodizing tanks have dimensional limits, and certain geometries may require special fixturing or agitation to ensure uniform coatings.
- Environmental and Regulatory Concerns: With increasing focus on sustainability, chromic acid anodizing may be restricted, and eco-friendly anodizing solutions are gaining traction.
- Budget: Higher performance coatings (like hard anodizing) may be more expensive due to specialized equipment and stricter process controls.
Aluminum anodizing significantly improves durability and aesthetics, but it’s important to weigh the process’s limitations. The maximum part size is dictated by anodizing tank dimensions—standard tanks often accommodate parts up to 4–6 feet long, which can be restrictive for oversized panels or complex assemblies. While anodizing dramatically enhances corrosion resistance, the anodic film is not invulnerable to strong acids, alkalis, or extreme temperatures. Maintenance, cleaning agents, and the specific application environment should all be considered. Additionally, the cost of anodizing is typically higher than basic painting or powder coating, with pricing influenced by part size, geometry, specified thickness, and color customization.
Need to calculate the cost of anodizing for your project? Request a custom anodizing quote now and get a detailed breakdown from multiple suppliers.
Overcoming Aluminum Anodizing Limitations with Innovation
The aluminum finishing industry is rapidly evolving to address the traditional limitations of anodizing. Recent innovations are expanding possibilities for manufacturers, architects, and product designers:
- Large-Scale and Complex Geometry Anodizing: Next-generation anodizing facilities are equipped with oversized tanks and advanced agitation systems, enabling uniform coatings for large architectural panels, automotive body parts, and intricate aerospace components.
- Process Automation & Digital Monitoring: New process control systems utilize real-time sensors, AI-driven analytics, and automated dosing, ensuring consistent coating thickness and quality even on high-volume production runs.
- Pre-Treatment Advancements: Enhanced cleaning, surface etching, and proprietary pre-treatment chemistries improve anodic layer adhesion, especially on cast or alloyed aluminum parts that previously posed challenges.
- Eco-Friendly Electrolytes: The adoption of citric acid-based or organic acid electrolytes reduces environmental impact by minimizing hazardous waste and enabling safer disposal practices.
- Hybrid and Composite Coatings: Combining anodizing with plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO), sol-gel, or nano-coatings delivers multi-functional surfaces—such as enhanced UV resistance, hydrophobicity, or antibacterial properties.
Rules and Regulations Regarding Aluminum Anodizing
Strict regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards are critical in the aluminum anodizing sector to ensure product quality, environmental stewardship, and worker safety. Here are the primary areas of focus:
- Environmental Protection: Regulations such as the Clean Water Act (CWA) and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States require anodizing facilities to minimize the release of hazardous chemicals and properly treat wastewater before discharge. Many companies implement closed-loop water recycling and advanced filtration systems to reduce environmental impact.
- Worker Safety: Handling of corrosive and toxic chemicals (e.g., sulfuric acid, chromic acid) necessitates strict occupational safety measures, including personal protective equipment (PPE), fume extraction, and regular employee training. Compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines is mandatory in the U.S.
- ISO and Industry Standards: Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), and ISO 7599/10074 (anodizing for architectural and industrial applications) help ensure consistent quality and performance across products.
- International and Regional Regulations: Anodizers must also adhere to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives in Europe, which restrict the use of specific chemicals in manufacturing.
By following these rules and regulations, aluminum anodizing companies protect worker health and safety, maintain product consistency, and contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Benefits of Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum anodizing delivers a wealth of benefits that make it a top choice for enhancing the performance, lifespan, and appearance of aluminum products. Key advantages include:
- Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: The anodic oxide layer acts as a tough barrier, protecting the base metal from moisture, salt, and harsh chemicals—ideal for outdoor, marine, or industrial environments.
- Increased Surface Hardness & Wear Resistance: Anodized aluminum surfaces can be up to three times harder than raw aluminum, making them highly resistant to scratches, abrasion, and general wear.
- Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Anodized aluminum can be dyed in a broad spectrum of colors, from vivid hues to metallic tones, offering architects and designers creative freedom for branding or decorative finishes.
- Lightweight and Non-Conductive: The process adds minimal weight, preserving aluminum’s inherent lightness. The oxide layer is also naturally non-conductive, which is useful for electrical insulation in electronics and power distribution applications.
- Low Maintenance & Cost-Effective: Anodized surfaces are easy to clean and do not peel, chip, or flake like paint. This translates to lower lifecycle costs by reducing the frequency of repairs or replacements.
- Environmentally Friendly: Compared to plating or painting, anodizing produces little waste and uses no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it an eco-conscious surface treatment.
Advantages of Aluminum Anodizing over Competing Processes
When comparing aluminum anodizing to other surface finishing methods such as electroplating, painting, or physical vapor deposition (PVD), anodizing consistently delivers superior results for a wide range of performance-critical applications:
- Durability & Hardness: The anodic oxide layer is integral to the aluminum, not just a surface deposit, so it won’t peel or flake. It provides greater hardness and longevity than most metallic platings or organic coatings.
- Corrosion Protection: Anodized aluminum outperforms painted and plated surfaces in harsh or corrosive environments, making it the preferred choice for marine, architectural, and industrial uses.
- Color Versatility: Unlike plating, which is often limited to metallic finishes, anodizing offers a wide palette of vibrant, UV-stable colors—ideal for branding and decorative applications.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Anodizing generates less hazardous waste and avoids the use of heavy metals found in many electroplating baths. It’s also free of VOCs, unlike many paints and powder coatings.
- Thermal and Electrical Properties: Anodized surfaces can be engineered for electrical insulation (Type II/III) or conductivity (Type I), and offer improved thermal emissivity for heat dissipation in electronics or lighting.
- Minimal Dimensional Change: The process adds only a thin oxide layer, preserving tight tolerances and critical dimensions important for aerospace and precision engineering.
Not sure which surface finishing process is right for your project? Compare anodizing vs. plating, painting, and PVD in our in-depth guide.
Applications of Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum anodizing is a cornerstone technology across diverse industries, delivering tailored solutions for both functional and decorative needs. Here are some of the top sectors and use cases:
- Architecture & Construction: Anodized aluminum is extensively used for curtain wall systems, window frames, cladding, railings, and signage. The durable anodic finish resists UV fading, corrosion, and staining—ideal for both exterior and interior architectural elements.
- Aerospace: Aerospace manufacturers rely on anodized aluminum for aircraft fuselage panels, wing structures, landing gear, and fasteners. The process delivers the required combination of lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue performance.
- Automotive: In the automotive sector, anodized aluminum is used for wheels, trim, roof rails, pedals, and engine components. The finish provides a sleek appearance and stands up to road salts, weathering, and repeated handling.
- Electronics & Electrical: Enclosures, heat sinks, connectors, and hardware in smartphones, laptops, and industrial equipment benefit from anodizing’s electrical properties, heat dissipation, and corrosion protection. Type I anodizing is especially valued for conductive applications.
- Medical Devices: The biocompatibility, sterilizability, and corrosion resistance of anodized aluminum make it ideal for surgical instruments, dental tools, orthopedic implants, and diagnostics equipment.
- Consumer Goods: Anodized aluminum enhances cookware, sporting goods, jewelry, bicycle frames, and personal electronics with attractive, wear-resistant finishes that are easy to clean and maintain.
- Military & Defense: Firearms, military vehicles, optical housings, and field equipment utilize hard anodized surfaces for exceptional durability in the harshest conditions.
- Marine Applications: Boat fittings, masts, hulls, and deck hardware are protected from saltwater and biofouling through anodizing’s robust corrosion defense.
- Packaging: Anodized aluminum is used in beverage cans, food containers, and cosmetic packaging for its sleek look, chemical resistance, and recyclability.
- Art & Decorative: Artists and fabricators use anodized aluminum for sculptures, signage, awards, and furniture to achieve complex colors and textures that last for decades.
The Future of Aluminum Anodizing
The future of aluminum anodizing is being shaped by rapid advances in materials science, process control, and environmental responsibility. Key trends and innovations driving the industry forward include:
- Smart Process Automation: AI-driven monitoring, predictive maintenance, and robotics are enabling higher throughput, lower defect rates, and consistent quality in modern anodizing lines.
- Next-Generation Coatings: Research is focused on multi-layered, composite, or nano-structured anodic films that offer additional functionalities, such as improved scratch resistance, anti-microbial properties, or enhanced thermal management.
- Eco-Friendly Chemistry: The industry is moving towards non-toxic, biodegradable electrolyte solutions and closed-loop systems to minimize water and energy usage, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Advanced Surface Customization: Customized surface texturing, photo-anodizing, and digital printing techniques are being integrated with anodizing to create unique, high-value finishes for luxury goods and high-tech devices.
- Integration with Additive Manufacturing: As 3D-printed aluminum parts become mainstream, new anodizing protocols are being developed to maximize performance and finish quality for complex geometries.
As demand grows for lightweight, durable, and sustainable materials, aluminum anodizing will play a pivotal role in industries ranging from automotive electrification to renewable energy, medical technology, and beyond.
Choosing the Correct Aluminum Anodizing Business
Finding the right aluminum anodizing company is essential for ensuring the success of your project—whether you need small-batch decorative parts, high-volume industrial runs, or precision aerospace components. Here’s how to make an informed decision:
- Capabilities & Certifications: Evaluate if the company offers the anodizing processes, tank sizes, and color options your project requires. Look for ISO, NADCAP, or other industry certifications that demonstrate quality and regulatory compliance.
- Industry Experience: Check for case studies or references relevant to your sector (e.g., aerospace, medical, electronics, architecture) to ensure the company understands your specific needs.
- Turnaround Time & Scalability: Consider lead times and whether the supplier can handle rush orders or scale up for full production.
- Value-Added Services: Some anodizers offer masking, CNC machining, assembly, or logistics support, streamlining your supply chain.
- Customer Service & Support: Responsive technical support, clear communication, and robust after-sales service are critical for a smooth experience.
Ready to compare top aluminum anodizing companies? Explore our comprehensive directory of aluminum anodizing services. Each listing features a detailed company profile with service offerings, certifications, sample projects, and a contact form for RFQs or technical inquiries. Our exclusive website previewer helps you quickly identify specialists for your application, and our streamlined RFQ form lets you reach out to multiple suppliers with a single request.
Have more questions about choosing an anodizing partner or the right process for your project? Contact our anodizing experts today for a customized consultation.
What is the aluminum anodizing process and how does it work?
Aluminum anodizing is an electrochemical process where an aluminum part is submerged in an electrolyte solution, and an electric current is passed through it, causing the surface to oxidize and form a durable, corrosion-resistant aluminum oxide layer that is integral to the metal itself.
What are the main types of aluminum anodizing and their uses?
The main types of anodizing are Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (Type II), Chromic Acid Anodizing (Type I), and Hard Anodizing (Type III). Type II is popular for general industry and decorative applications, Type I is favored in electronics and aerospace for conductivity, and Type III is used in precision engineering and defense for maximum hardness and wear resistance.
What factors should be considered when choosing an aluminum anodizing process?
Key factors include desired properties like corrosion resistance, hardness, electrical insulation, intended use and industry standards, part design and geometry, environmental and regulatory concerns, and overall budget. These influence which anodizing method and specifications will best suit your project.
What are the main benefits of aluminum anodizing?
Benefits include exceptional corrosion resistance, increased surface hardness and wear resistance, enhanced aesthetic options, lightweight and non-conductive qualities, low maintenance, cost-effectiveness over the lifecycle, and an environmentally friendly process compared to alternatives.
How does aluminum anodizing compare to other finishing processes like plating or painting?
Aluminum anodizing generally offers greater durability, corrosion protection, color versatility, and eco-friendliness compared to plating or painting. The anodic oxide layer is integral to the metal and doesn’t peel or flake, while allowing more color options and minimizing hazardous waste.
What are some common applications for anodized aluminum?
Anodized aluminum is widely used in architecture, aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, military equipment, marine hardware, packaging, and art or decorative projects due to its durability, aesthetics, and specialized properties.
What regulations and standards apply to aluminum anodizing companies?
Aluminum anodizing companies must comply with regulations such as the Clean Water Act (CWA), Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), OSHA safety standards, ISO 9001/14001/7599 certifications, and directives like REACH and RoHS to protect workers, the environment, and ensure product quality.





 Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum Anodizing EDM
EDM Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless Nickel Plating EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Heat Treating
Heat Treating Metal Coating Services
Metal Coating Services Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services