To understand how a metal can be dyed black, the basic process of anodization should be understood. Anodizing involves using a corrosive chemical and electrical current to alter the chemical body of certain metals and make them stronger in the process. Read More…
At Tompkins Metal Finishing, we offer mid to high volume aluminum anodizing. We do pre-cleaning, etching, deoxidizng, dyeing and sealing. We can achieve a wide range of surface finishes from bright to dull matte in clear, black, gold, blue and red. Other methods are also available with consideration of alloy, coating thickness, masking requirements and racking instructions.
Pioneer offers many custom finishing solutions to make your products perform at the highest levels. We are experts in providing specialized finishes to improve the performance for your specific component parts. Whether your product design requirements include finishes to make your product resist corrosion, last longer, look better, slide more freely, bond securely to another material, or many...

At All Metals Processing of Orange County, we specialize in providing high-quality aluminum anodizing services that enhance both the performance and appearance of metal components. We take pride in our ability to deliver precise, consistent finishes that improve corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal across a wide range of applications.

At Automatic Anodizing, we specialize in providing high-quality aluminum anodizing services designed to enhance both the appearance and performance of aluminum parts. With decades of experience, we have built a reputation for precision, consistency, and reliability in every project we handle. Our advanced anodizing processes improve corrosion resistance, wear protection, and surface hardness...

Dajcor Aluminum is the leading Canadian supplier of extruded, fabricated/machined and anodized components and assemblies to the automotive, renewable energy, transportation, building trades, military, recreation, and consumer-product industries.
More Black Anodizing Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Anodizing Acids and Black Anodizing Processes
Anodizing is a transformative electrochemical process that significantly enhances the properties of various metals, most notably aluminum, titanium, magnesium, and zinc. By carefully controlling the anodizing process and the acids used, manufacturers can improve metal strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appearance, making anodizing a crucial surface finishing method in industries ranging from aerospace to consumer electronics.
Types of Anodizing Acids: Methods, Applications, and Advantages
When exploring anodizing techniques, it’s essential to understand the different types of acids employed in the process and their unique benefits. Each acid type is suited for specific applications, tailored to the desired finish, metal substrate, and performance requirements. The primary anodizing acids include:
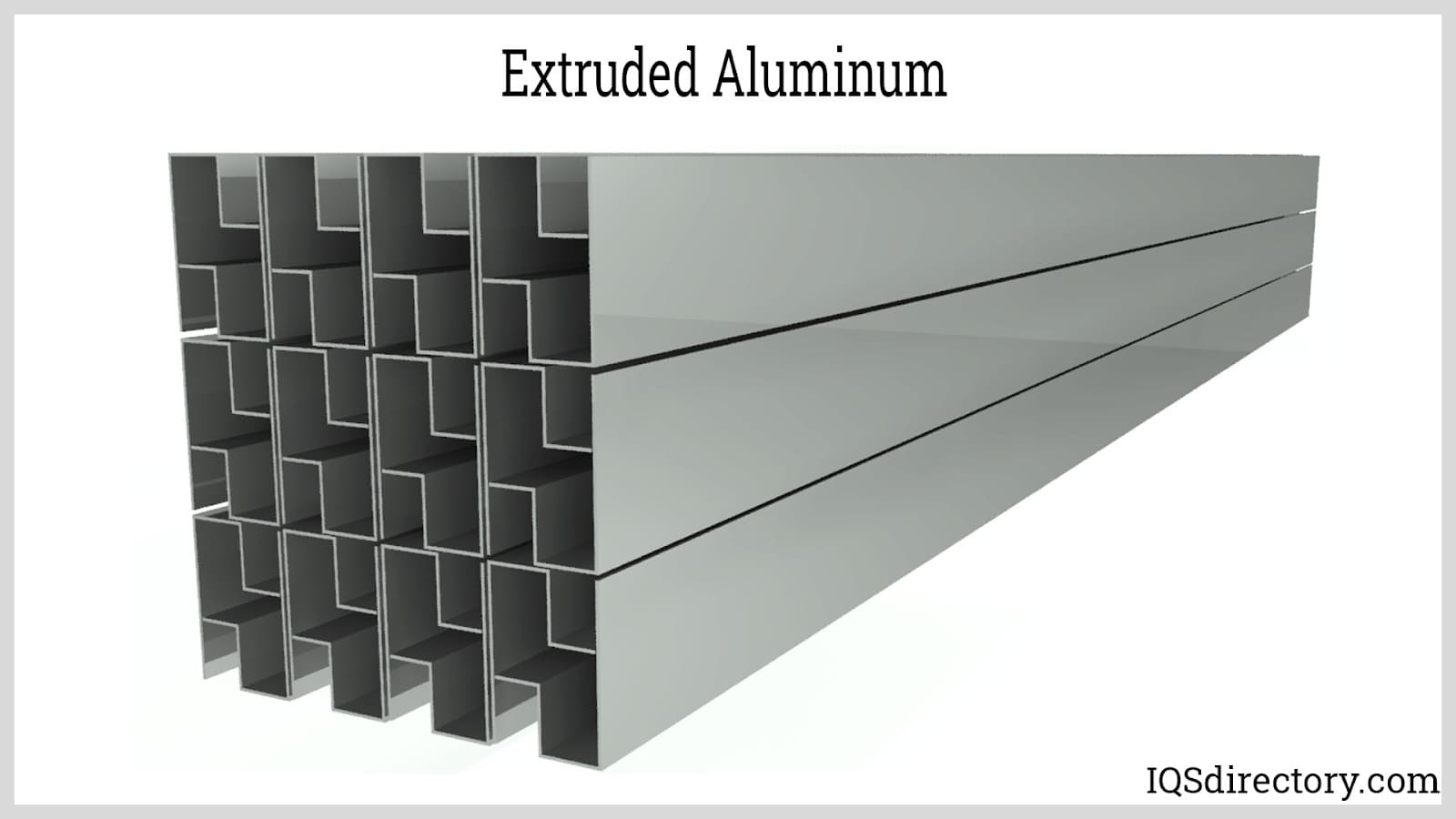
- Sulfuric Acid Anodizing – The most commonly used method for aluminum anodizing, sulfuric acid anodizing produces a durable, porous oxide layer that is ideal for dye absorption and provides excellent corrosion resistance. Sulfuric acid anodizing is suitable for a wide range of architectural, automotive, and industrial components.
- Chromic Acid Anodizing – Chromic acid is often utilized when a thinner oxide layer is required, providing excellent corrosion resistance while maintaining dimensional tolerances. This process is frequently used in aerospace and defense applications where fatigue strength and surface integrity are critical.
- Phosphoric Acid Anodizing – While less common, phosphoric acid anodizing is primarily used for adhesive bonding applications, improving the bonding strength of paints and adhesives, especially in the aerospace sector.
- Organic and Boric Acid Anodizing – These acids are often reserved for custom anodizing requirements, such as precise coloring or when more control over the process is required. Boric-sulfuric acid anodizing, for example, is emerging as an environmentally friendly alternative, replacing chromic acid in some aerospace applications.
Looking for detailed comparisons? Explore the various types of anodizing processes and their specific advantages.
Metals Commonly Anodized: Which Materials Benefit Most?
Anodizing is not limited to aluminum, though aluminum anodizing remains the industry standard due to its widespread use and favorable oxide layer characteristics. Here’s a closer look at metals frequently subjected to anodizing:
- Aluminum – Provides a hard, corrosion-resistant, and decorative oxide surface. Key for architectural panels, automotive parts, cookware, and electronic housings.
- Titanium – Yields vibrant colors due to interference effects and is widely used in medical devices, aerospace fasteners, and jewelry.
- Magnesium – Increases corrosion resistance and surface hardness, important for lightweight automotive and aerospace parts.
- Zinc – Less common but anodized for specialized corrosion resistance and decorative finishes.
Curious about which metals are best suited for your anodizing needs? Discover the materials most compatible with anodizing.
Key Benefits of Anodizing: Why Choose Anodized Finishes?
Anodizing offers a wealth of advantages over traditional surface treatments such as painting, powder coating, or electroplating. Some of the core benefits include:
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: The anodized layer acts as a protective barrier, significantly improving resistance to environmental wear, chemicals, and salt spray.
- Increased Surface Hardness: Anodized metals exhibit higher surface hardness and abrasion resistance, extending product lifespan.
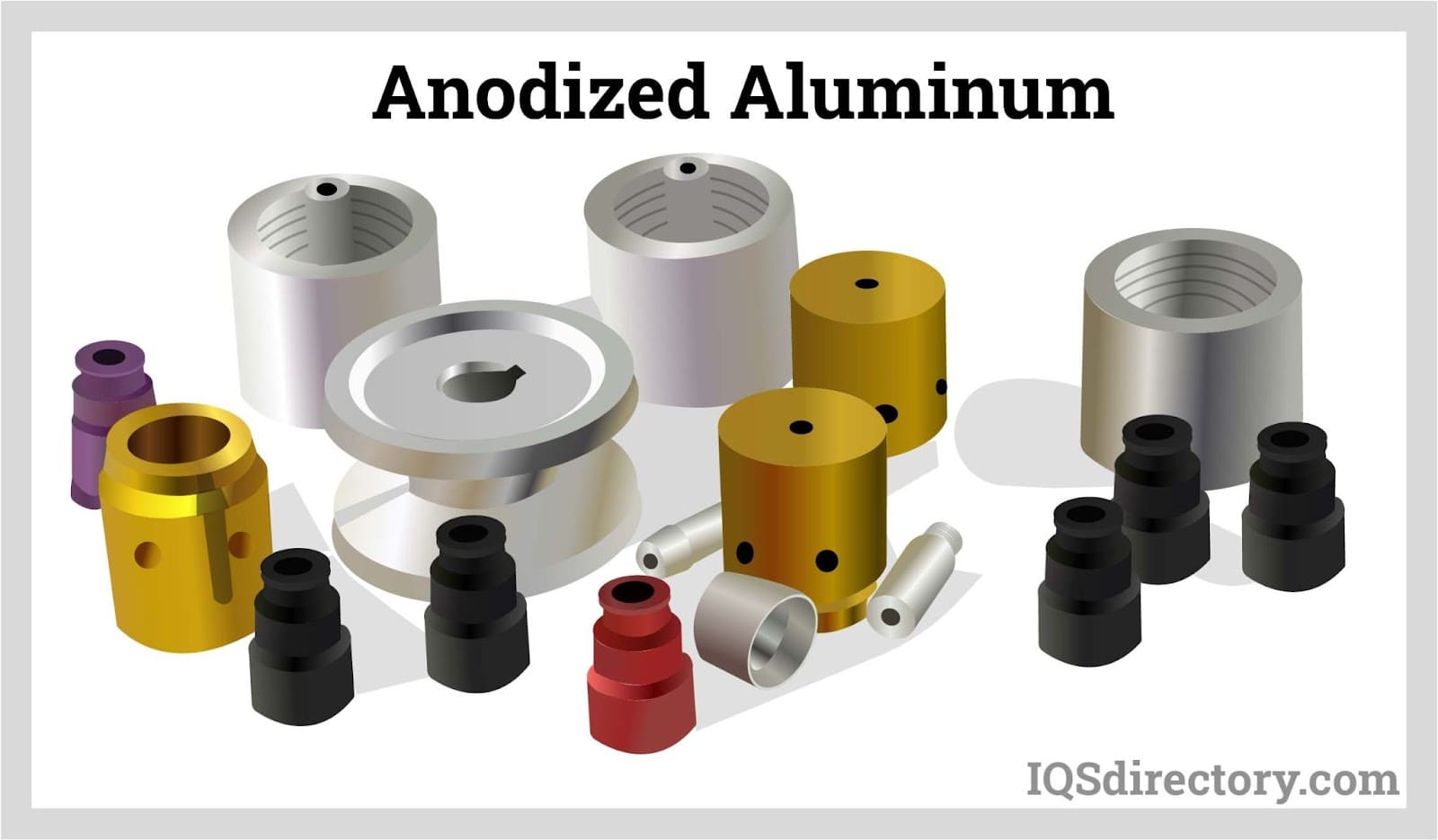
- Improved Aesthetics and Color Variety: The porous oxide layer allows for vivid and long-lasting dye colors, including black anodized finishes, bright metallic hues, and custom colors.
- Environmentally Friendly: Certain anodizing processes, such as boric-sulfuric acid anodizing, are less harmful than traditional plating methods and produce minimal hazardous waste.
- Adhesion for Paints and Adhesives: The anodized surface provides an ideal texture for subsequent painting or bonding, critical for aerospace and automotive assemblies.
Understanding the Black Anodizing Process: Steps, Dyes, and Technology
Black anodizing is among the most sought-after finishes for both functional and decorative applications. Its deep, rich color and outstanding durability make it a preferred choice for electronics, automotive trim, architectural hardware, and more. But how is black anodizing achieved, and what makes it unique compared to other colors?
How Black Anodizing Works: The Step-by-Step Process
- Surface Preparation: The metal part is thoroughly cleaned, degreased, and etched to ensure a contaminant-free surface, which is essential for uniform anodizing and dye uptake.
- Anodizing Bath: The prepared part is submerged in an electrolyte solution—most commonly sulfuric acid—where an electric current is applied. This process forms a porous oxide layer on the metal’s surface.
- Dye Immersion: Immediately after anodizing, the porous aluminum oxide layer is immersed in a black dye bath. The dye penetrates the pores, resulting in a deep, uniform black finish. Black dyes can be either organic or inorganic, with inorganic dyes such as ferric ammonium oxalate and gold-based compounds offering superior lightfastness and UV resistance.
- Sealing: The dyed component is sealed using hot water or steam, sometimes with nickel acetate. Sealing hydrates the oxide layer, locking in color, enhancing corrosion resistance, and preventing dye leaching or fading.
- Final Inspection and Quality Control: Parts undergo rigorous inspection to ensure color consistency, surface integrity, and adherence to specifications.
Interested in the science behind color anodizing? Learn more about dye chemistry and anodized color options.
Black Anodizing Dyes: Organic vs. Inorganic
Choosing the right black dye is critical for achieving the desired performance, appearance, and longevity. Here’s how the options compare:
- Inorganic Dyes (Ferric Ammonium Oxalate, Gold Dye): These dyes are exceptionally lightfast, meaning they resist UV fading and maintain color vibrancy over time. Ideal for outdoor, automotive, and aerospace applications.
- Organic Dyes: While organic dyes provide a wider range of customizable black hues and are suitable for many consumer products, they may show some fading when exposed to prolonged sunlight or harsh environments.
- Electrolytic Coloring: Black coloration can also be achieved by electrolytically depositing metal salts (such as tin or cobalt) in the anodic pores, resulting in a rich, metallic black that is highly durable and fade-resistant.
Wondering which dye is best for your project? Compare anodizing dye technologies and their benefits.
Applications of Black Anodizing: Where and Why Is It Used?
Black anodized finishes are in high demand across a variety of industries because of their unique combination of aesthetics and performance. Common applications include:
- Consumer Electronics: Black anodized aluminum is ubiquitous in smartphones, laptops, MP3 players, cameras, and flashlights, providing sleek looks and fingerprint resistance.
- Automotive & Motorsports: Used for trim, wheels, engine parts, pedals, and performance hardware, black anodizing offers both style and durability under harsh conditions.
- Aerospace & Defense: Black anodized components provide non-reflective, corrosion-resistant finishes critical for cockpit controls, instrument housings, and structural elements.
- Architectural Hardware: Door handles, window frames, and signage often employ black anodized aluminum for modern design and weather resistance.
- Cookware & Kitchen Equipment: Two-tone and all-black anodized pots, pans, and utensils deliver superior non-stick surfaces and corrosion protection.
- Medical Devices: Precision instruments and cases utilize black anodizing for biocompatibility, ease of sterilization, and clear part differentiation.
Have a specific application in mind? Explore how black anodizing can enhance your products.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right Anodizing Process for Your Product
If you’re evaluating anodizing services for your manufacturing or product development needs, consider these critical factors to ensure you select the optimal process and finish:
- Metal Substrate: Different metals respond uniquely to anodizing. Aluminum alloys, for example, may require specific process parameters for uniform color and optimal hardness.
- Intended Use and Environment: Will the part be exposed to harsh weather, chemicals, or UV light? Black anodizing with inorganic dyes is best for outdoor and high-performance applications.
- Color and Appearance: Is a deep, matte black required, or will another color suit your design? Consider the availability of custom colors and gloss levels.
- Thickness and Tolerance: Different anodizing methods yield varying oxide layer thickness. Sulfuric acid anodizing allows for greater thickness control, while chromic acid is preferred for thin, precise coatings.
- Cost and Turnaround Time: Some methods are faster or more economical for large production runs. Discuss your project volume and budget with your anodizing provider.
- Regulatory and Environmental Considerations: For industries like aerospace and medical, compliance with RoHS, REACH, or FDA guidelines may be required. Environmentally friendly processes like boric-sulfuric acid anodizing should be considered where green manufacturing is a priority.
Need help selecting the right anodizing solution? Speak with an anodizing specialist for tailored recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Anodizing and Black Anodizing
- What is the difference between hard anodizing and decorative anodizing?
Hard anodizing (Type III) produces a much thicker, harder oxide layer than standard (Type II) decorative anodizing, making it ideal for industrial, aerospace, and military parts that require maximum wear resistance and protection. - Can anodized surfaces be repaired if damaged?
Minor scratches can sometimes be buffed, but deep gouges or corrosion typically require stripping and re-anodizing. Maintenance guidelines vary by application—consult your anodizing service provider for best practices. - How does anodizing compare to powder coating or painting?
Anodizing integrates the protective layer into the metal itself, making it more durable and long-lasting than coatings that sit on top. Anodized finishes also retain their metallic look and are less prone to chipping or flaking. - Is black anodizing safe for food contact surfaces?
Yes—when performed according to FDA guidelines, black anodized aluminum is non-toxic and safe for cookware and food processing equipment. - What maintenance is required for black anodized parts?
Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is usually sufficient. Avoid abrasive cleaners that can dull the finish or damage the oxide layer.
Advanced Anodizing Technologies: Innovations and Trends
The anodizing industry continues to advance, with new technologies emerging to improve sustainability, performance, and design flexibility. Recent trends include:
- Boric-Sulfuric Acid Anodizing (BSAA): An environmentally friendly alternative to chromic acid, offering excellent corrosion resistance without the hazards of hexavalent chromium.
- Pulse Anodizing: Enhanced process control and energy efficiency, resulting in more uniform coatings and reduced waste.
- Nanostructured Anodic Films: Engineered at the nanoscale for superior mechanical, electrical, and optical properties, opening new applications in electronics and photonics.
- Laser-Assisted Anodizing: Precision patterning and selective coloring capabilities for high-end consumer goods and scientific equipment.
- Customization in Color and Texture: Advanced anodizing allows for bespoke finishes, including multi-color gradients, branding, and anti-slip textures.
How to Get Started with Anodizing Services: Next Steps
Whether you’re a product designer, manufacturer, or engineer, partnering with an experienced anodizing company is essential to achieving the best results. Here’s how to begin:
- Define your performance, appearance, and regulatory requirements.
- Consult with anodizing specialists to select the right process, acid type, and finish for your application.
- Request samples or prototypes to evaluate appearance, durability, and fit.
- Review supplier credentials, quality certifications, and environmental compliance.
- Place your production order and establish ongoing quality assurance protocols.
Ready to get started? Request a quote for anodizing services or contact our team for expert guidance.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Full Potential of Anodized and Black Anodized Metals
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, anodizing stands out as a superior finishing process for metals, offering unmatched durability, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. Black anodized aluminum, in particular, delivers a blend of aesthetics and performance that’s difficult to rival—making it a top choice for electronics, automotive, aerospace, and architectural applications. By understanding the science, technology, and evolving trends in anodizing acids and processes, you can make informed decisions that boost product value and customer appeal.
If you’re considering anodizing for your next project, take the time to explore different acid types, finishes, and dyes to find the perfect match for your application. Leverage the expertise of industry-leading anodizing providers to maximize both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Ready to take the next step? Request a custom quote or talk to an anodizing expert for personalized advice on your anodizing project.





 Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum Anodizing EDM
EDM Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless Nickel Plating EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Heat Treating
Heat Treating Metal Coating Services
Metal Coating Services Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services